When you have children, you plan for their future like a responsible parent and the consequences of not doing so could put your own flesh and blood at risk. For IT companies their assets are the same. IT assets have a life cycle of their own and must be managed accordingly for the company to not be at risk of any security or financial issues. This IT asset life cycle has stages just like a growing individual from birth to senility to the inevitable grave. The stages of IT asset management are planning, procurement, deployment, usage, upgrade, decommission, salvage and disposition. Our focus will be on the retirement and funeral management of these machines that work tirelessly for their organizations.
All retirement homes and funerals are costly but that is not the same when it comes to IT assets because if the process is managed correctly that obsolete asset can give you returns or even profit. When cost effectiveness is required the finance department of an organization steps forward to bank, invest and ensure that it is achieved. An effective process for IT Asset Disposition (ITAD) would end up with some return. The minimal steps any finance department should take for End Of Life (EOL) IT assets management:
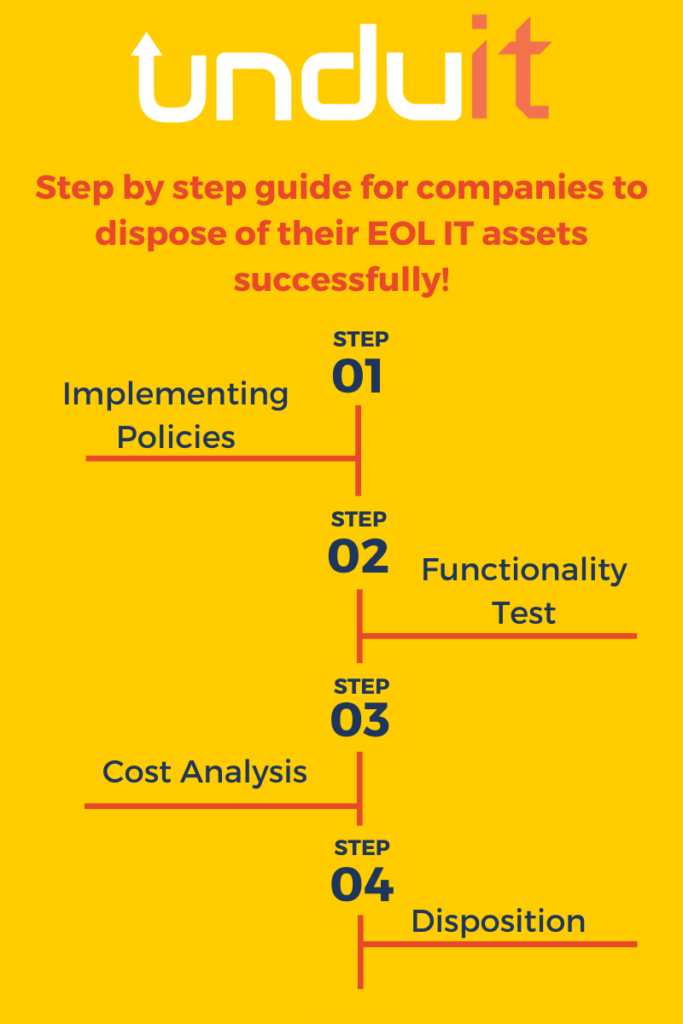
- Step by step guide for companies to dispose of their EOL IT assets successfully!Implement policies for ITAD Security preferably according to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and their own local data protection laws. This ensures that the disposed asset does not become a liability in the future for the organization.
- Prepare a checklist for functionality tests for all computing equipment present. This sets a grading system that can be used to categorize assets into three different ITAD subgroups:
- Reuse: this category does not only hold the whole asset into account rather parts of the asset can also be reused by the organization if need be. Like monitors, mice, keyboards, hard-drives, RAM and more.
- Salvage: should only be conducted with proper erasure software implantation first and then all salvaged parts should be sold off to invest into the replacement equipment.
- Dispose/recycle: Dispose of all assets using ITAD professionals to rule out all liability issues and breaching of national laws. If done using organizational resources, then the Basel Convention policies should be used to make sure that the e-waste is managed properly.
- After functionality assessment of the asset, reevaluate the comparative cost effectiveness by placing the asset in all three functional categories. This ensures whether over time the asset would yield more profit if reused, cost of parts salvaged would yield greater profit or disposal/recycling would be most cost effective.
- If disposal is the outcome of the functionality test, then the finance department should broker a deal with a single ITAD company to deal with all types of data disposals whether it being hardware or software. This will ensure that if any security breach occurs the organization would hold one ITAD company responsible rather than multiple. A long-term solution would be to set up an ITAD department for the organization to make the process of EOL IT asset management even more cost effective and potentially profitable.
Learn more about IT Asset Disposition in our comprehensive ITAD Guide